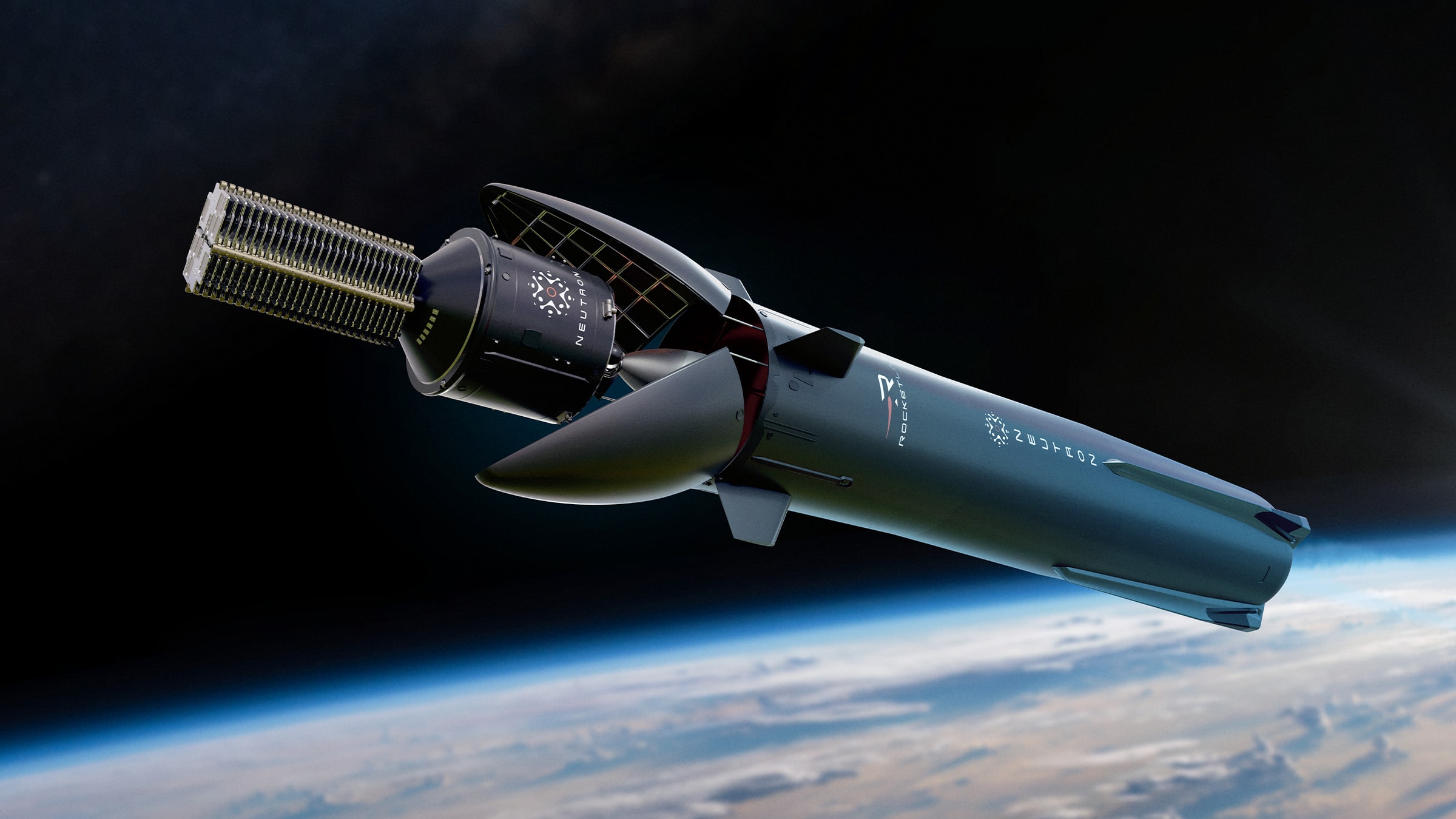
May 27, 2025 — In the fast-evolving landscape of space exploration, Rocket Lab has emerged as a trailblazer in providing reliable and cost-effective launch services for small satellites. Since its inception in 2006, the company has revolutionized access to space, enabling universities, governments, and commercial entities to deploy their payloads efficiently into orbit.
What Sets Rocket Lab Apart?
Rocket Lab specializes in launching small satellites—often referred to as CubeSats or smallsats—with its proprietary Electron rocket. This lightweight, two-stage launch vehicle is specifically designed to carry payloads weighing up to 300 kilograms into low Earth orbit (LEO). Unlike traditional heavy-lift rockets, Electron’s smaller size and reusable components allow for frequent and affordable launches, opening space opportunities for a wider range of customers.
One of Rocket Lab’s standout innovations is the use of electric pump-fed Rutherford engines, a first in the aerospace industry. This technology enhances efficiency and reduces launch costs, making space access more economical than ever before.
Notable Rocket Lab Missions
Rocket Lab has executed over 40 successful Electron launches to date, delivering satellites for diverse missions including Earth observation, communications, scientific research, and technology demonstrations.
Some recent high-profile missions include:
- Running Out of Fingers (ROOF) Mission (2024): A multi-satellite deployment campaign that delivered a constellation of CubeSats for environmental monitoring and disaster response applications.
- Photon Satellite Platform Launches: Rocket Lab has developed its own satellite platform called Photon, enabling rapid deployment of space payloads with integrated power and communication systems. Photon missions have supported lunar payloads, Earth imaging, and even deep-space exploration initiatives.
- CAPSTONE Mission Collaboration: Rocket Lab partnered with NASA to launch the CAPSTONE spacecraft, which is studying a unique lunar orbit to support the Artemis program’s Gateway lunar station.
Reusability and Sustainability Goals
In 2021, Rocket Lab made headlines with its efforts to develop a reusable first-stage booster for Electron rockets. By recovering and refurbishing rocket boosters, the company aims to reduce waste and lower launch costs further.
The first successful booster recovery occurred during the Return to Sender mission in 2022, with subsequent flights incorporating lessons learned to improve turnaround time and reliability.
Expanding Beyond Earth Orbit
While Rocket Lab initially focused on Earth orbit launches, its ambitions extend to deep space missions. The company announced plans to launch missions to the Moon and Mars, leveraging its Photon platform to enable small-scale planetary exploration and technology demonstrations.
In late 2023, Rocket Lab successfully launched its CAPSTONE mission, marking the first private company to send a spacecraft to lunar orbit.This achievement opened new opportunities for upcoming commercial missions outside Earth’s orbit.
Commercial and Government Partnerships
Rocket Lab caters to a wide range of clients, from commercial satellite companies and defense organizations to research institutions. Its ability to offer rapid, dedicated launches has made it a preferred partner for constellations seeking timely deployment.
Government collaborations include contracts with NASA, the US Space Force, and international space agencies, highlighting Rocket Lab’s growing influence in the global aerospace sector.
The Future of Rocket Lab Missions
Looking ahead, Rocket Lab plans to introduce its next-generation launch vehicle, Neutron, designed to carry heavier payloads and support crewed missions. Neutron will compete with larger rockets, aiming to offer flexibility and reliability for a broader range of space missions.
Rocket Lab also emphasizes sustainability, targeting carbon-neutral launches and developing technologies to mitigate space debris.
Conclusion
Rocket Lab’s innovative approach to small satellite launches is transforming the space industry by making orbital access more frequent, affordable, and versatile. As the company expands its mission portfolio from Earth orbit to the Moon and beyond, it continues to play a crucial role in democratizing space for scientific discovery, commercial growth, and exploration.